Price Floors Go Equilibrium And Result In A

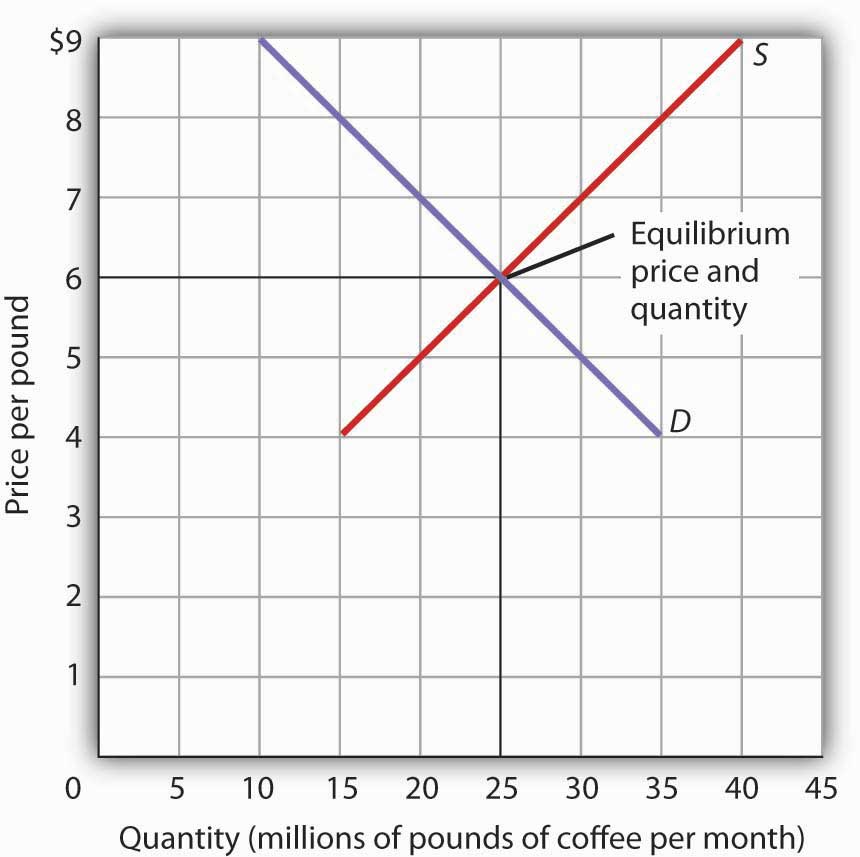
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
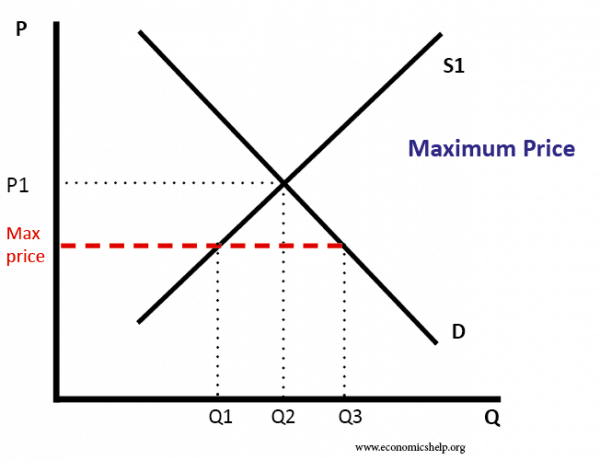
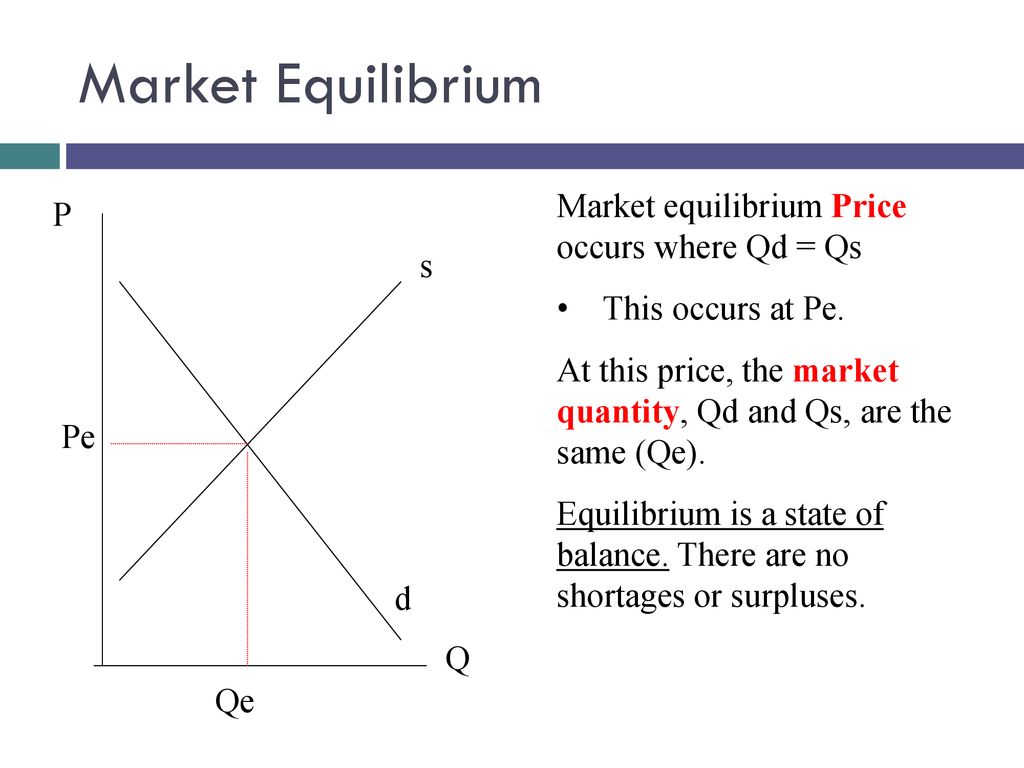
Price floors go equilibrium and result in a. The rock cannot go lower than the floor because it will hit the floor and stop. Quantity demanded at the price ceiling exceeds the amount at the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is less than the amount at the equilibrium price. This means the market s quantity supplied and quantity demanded will not equal each other resulting. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
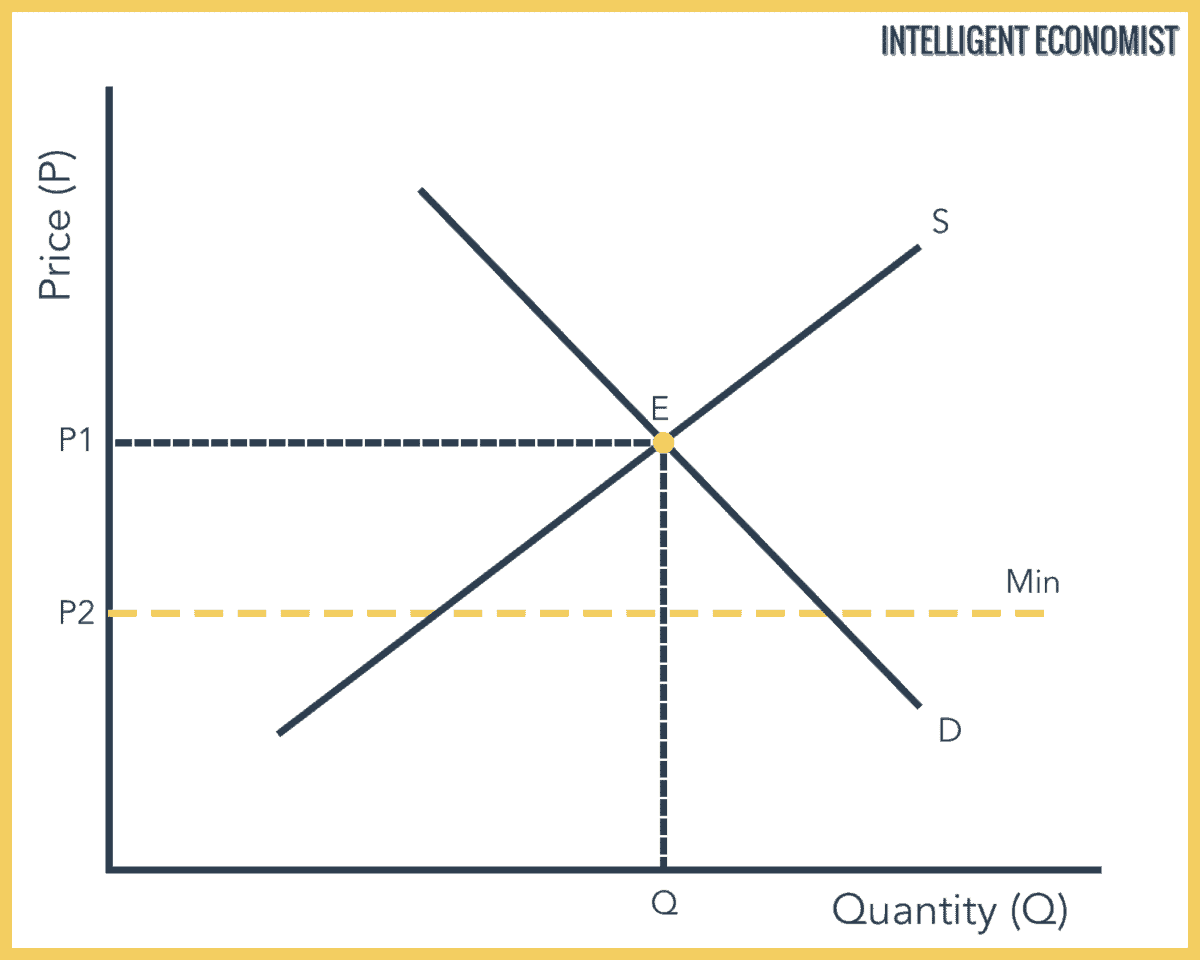
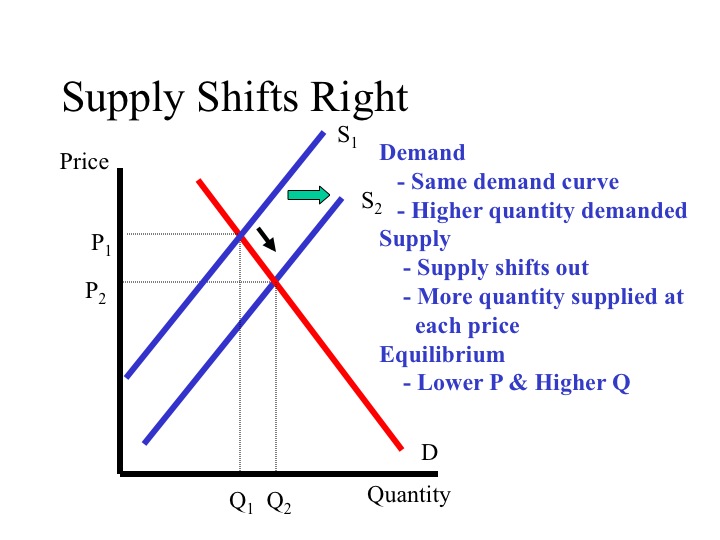
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor. When binding floors go above equilibrium and result in a surplus. Drawing a price floor is simple. If the price floor is above market equilibrium then companies are forced to sell at that price.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. Quantity supplied at the price floor exceeds the amount at the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is less than the amount at the equilibrium price. Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences. Where this gets tricky is that a binding price floor occurs above the equilibrium price.
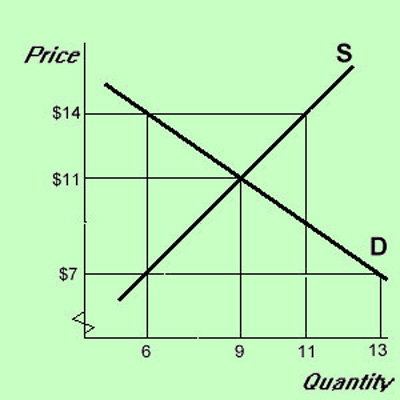
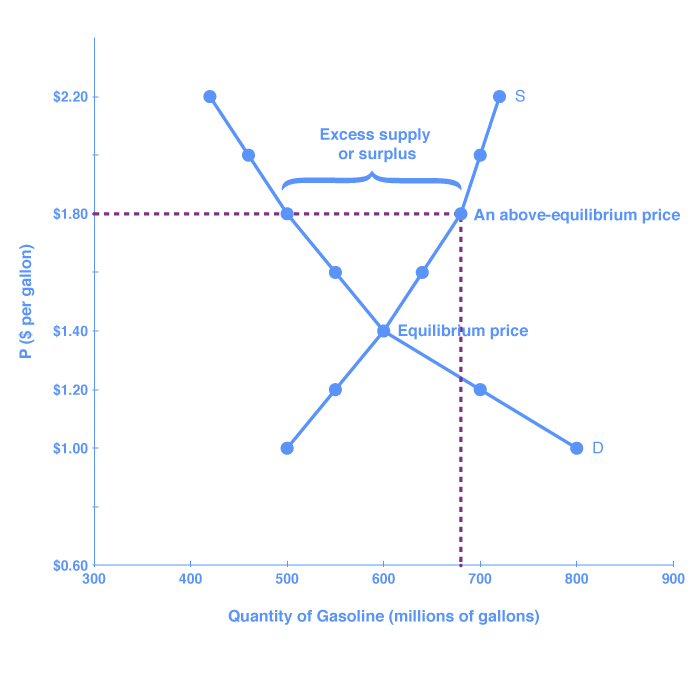
Government controls price floors go equilibrium and result in a price ceilings from ap gov. When binding ceilings go below equilibrium and result in a shortage. You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example. Apgov at cupertino high.
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. When they are set above the market price then there is a possibility that there will be an excess supply or a surplus. The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd.
Min legal price a seller can sell a product. The result of a binding price floor is. When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists. The price cannot go lower than the price floor.
Producers are better off as a result of the binding price floor if the higher price higher than equilibrium price makes up for the lower quantity sold. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result. To intuitively understand a price floor imagine dropping a rock in your house.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhyYouCantInfluenceGasPrices3-257334e47bc54cd7a449da9df90814af.png)