Price Floor Set Below Equilibrium
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
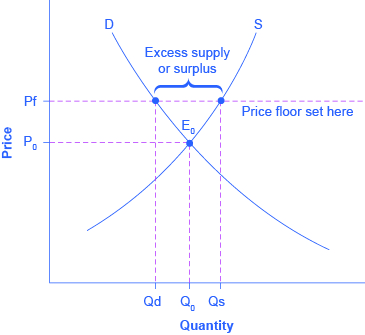
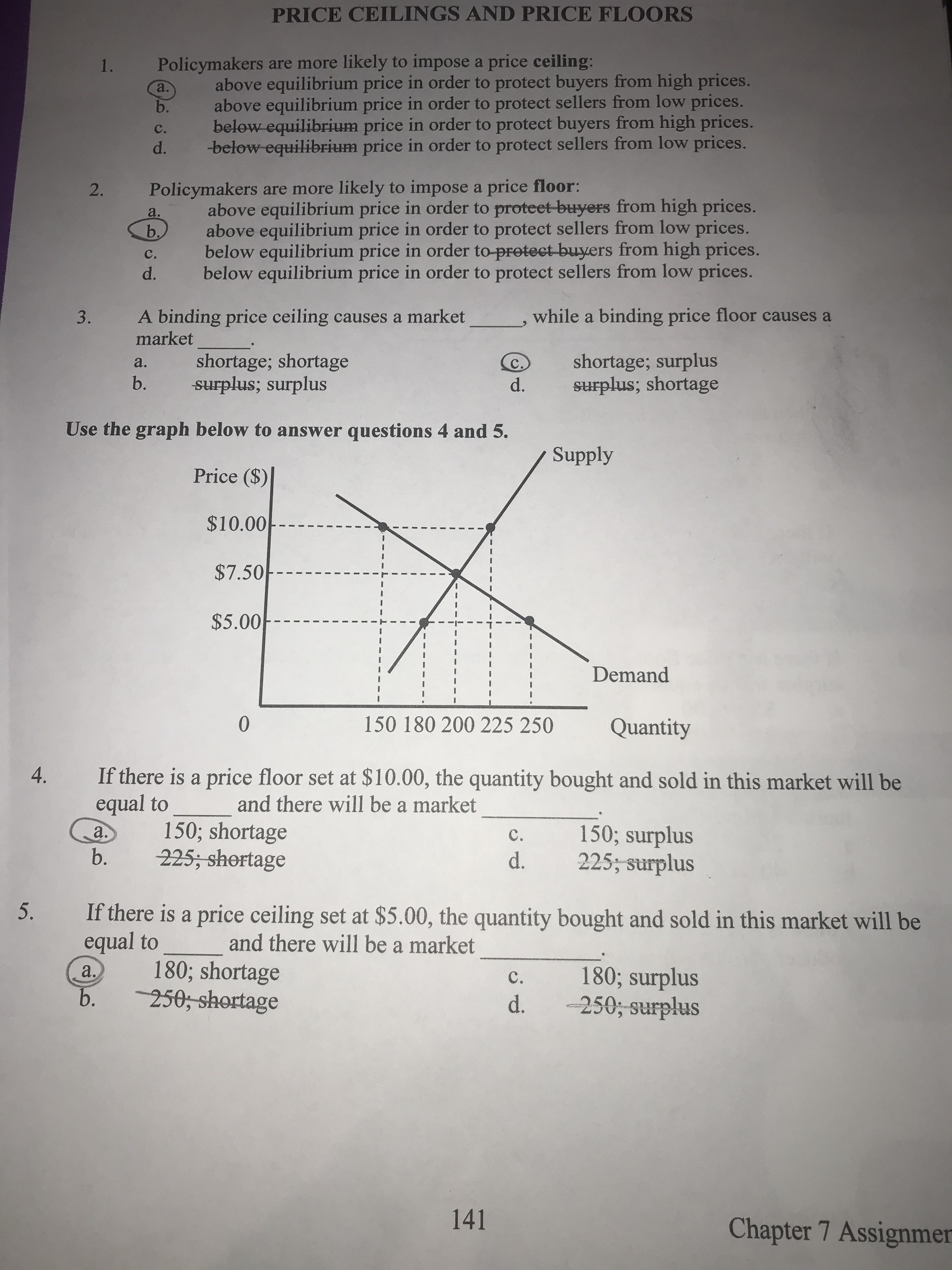
Price floor set below equilibrium. The conditions of demand and supply are given in the table below. Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price. The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd. When a price floor is put in place the price of a good will likely be set above equilibrium.
Drawing a price floor is simple. In contrast consumers demand for the commodity will decrease and supply surplus is generated. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. Price floors can also be set below equilibrium as a preventative measure in case prices are expected to decrease dramatically.
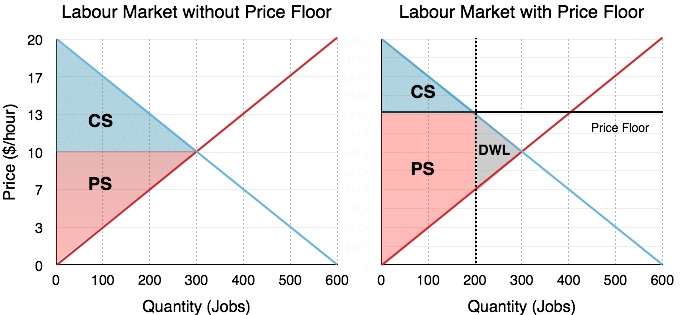
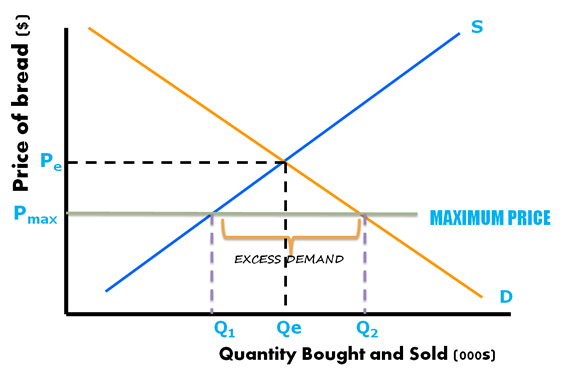
Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. That will create a surplus. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result. In such situations the quantity supplied of a good will exceed the quantity demanded resulting in a surplus.
A price ceiling set below the equilibrium price is an attempt to make the. Producers won t produce as much at the lower price while consumers will demand more because the goods are cheaper. In the first graph at right the dashed green line represents a price floor set below the free market price. If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
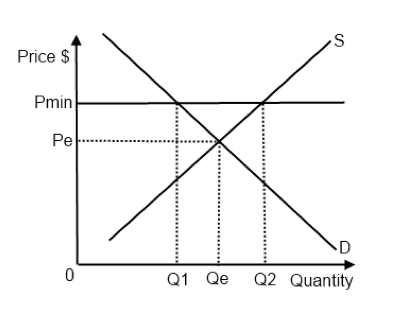
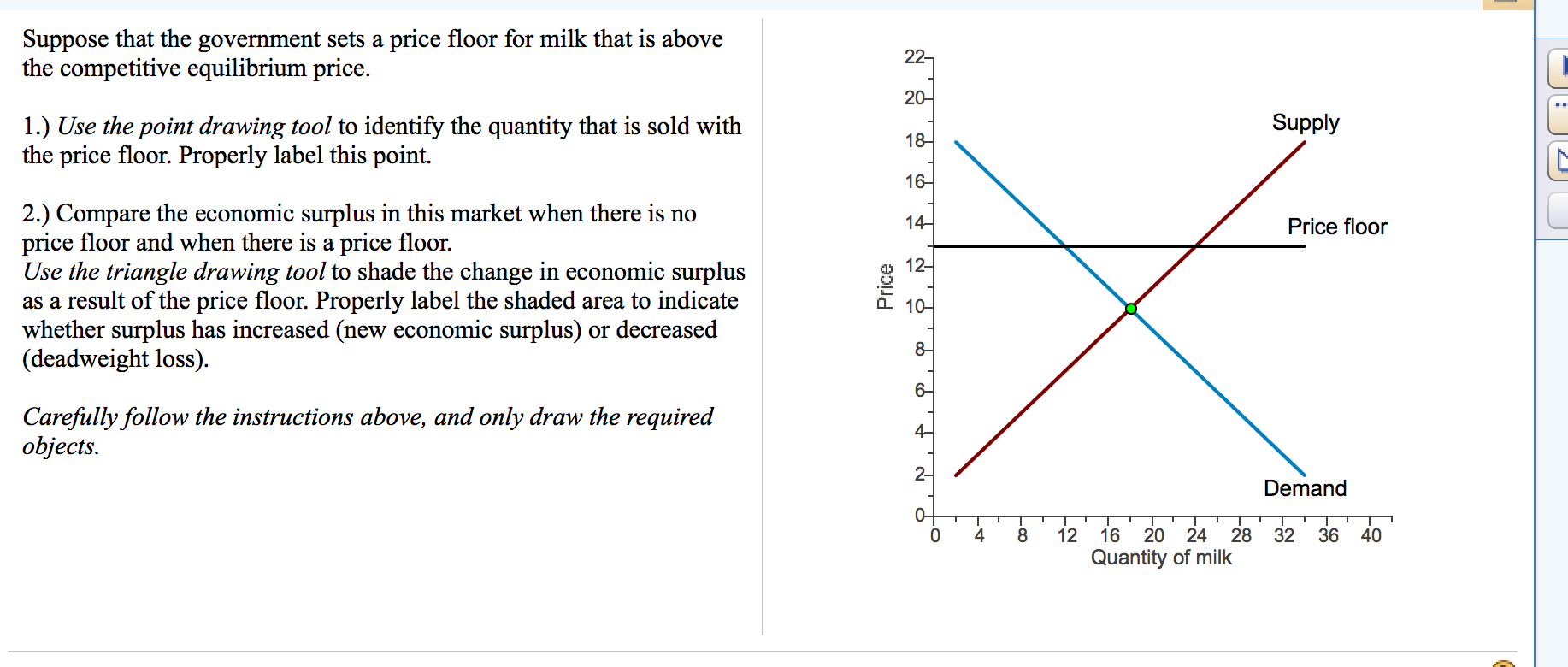
Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor. When the ceiling is set below the market price there will be excess demand or a supply shortage. At higher market price producers increase their supply.
But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed. How does a price floor set above the equilibrium level affect quantity demanded and quantity supplied. In this case the floor has no practical effect. For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
A price floor could be set below the free market equilibrium price. By increasing the price the quantity demanded will fall and the quantity supplied will rise. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level.
The government has mandated a minimum price but the market already bears and is using a higher price. When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists.