Price Floor In The Market For Wheat

This is the currently selected item.
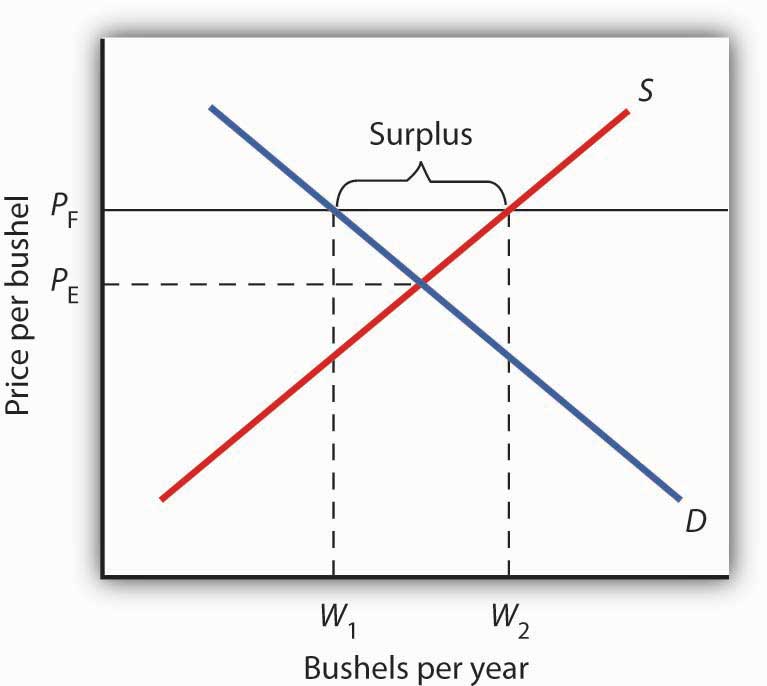
Price floor in the market for wheat. Market interventions and deadweight loss. However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling. A quantity demanded will decrease. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd.
Decreases the price paid by consumers. A whether the equilibrium price is lower than the price floor and b relative elasticity of demand to supply. A price floor example. D the price floor will not affect the market price or output.
A price floor example. Let s consider the market for wheat in a developing country. B quantity supplied will increase. A price floor for wheat creates a surplus of wheat equal to w2 w1 bushels.
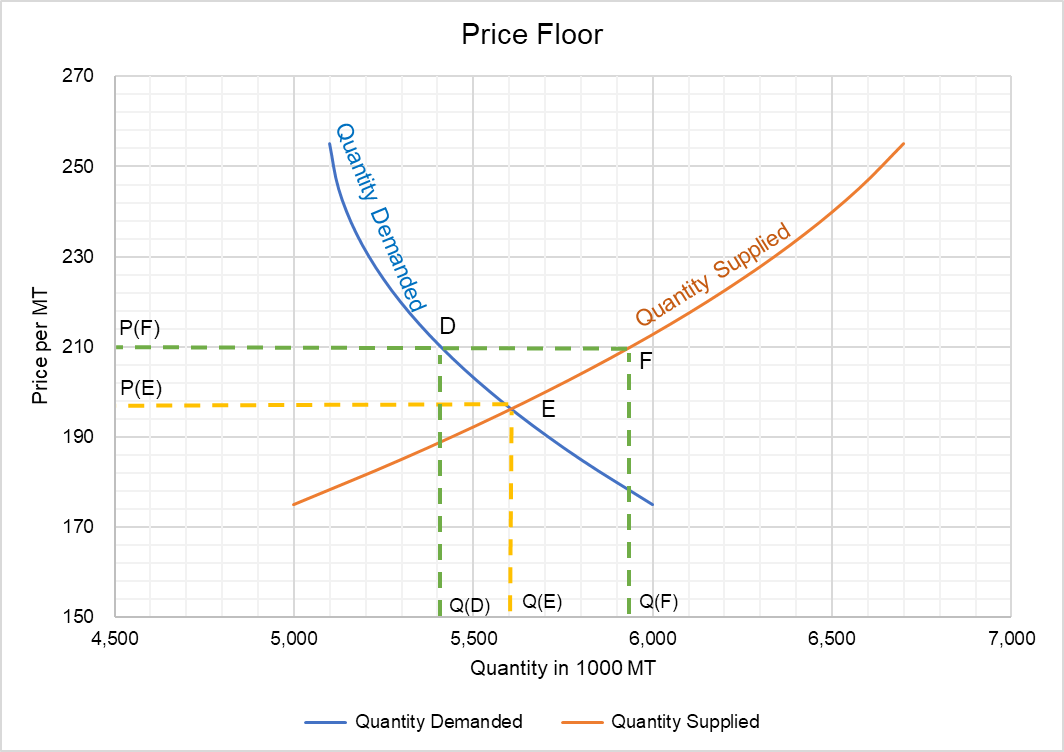
Price ceilings and price floors. The government has imposed a minimum price of 210 per metric ton of wheat. If the government imposes a price floor in the market at a price of 0 40 per pound. Refer to the figure below depicting a 10 price floor on the market for wheat.
Decreases the price received by farmers. The actual impact of a price floor on the market depends on two factors. The market for apples is in equilibrium at a price of 0 50 per pound. Minimum wage and price floors.
Use this graph for part c through e. Price and quantity controls. Increases the price paid by consumers. The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
How price controls reallocate surplus. A price floor in the market for wheat. Wheat is a versatile grain that can be grown in a variety of climates and dates back to 10 000 b c. The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
The effect of government interventions on surplus. Does not change the price received by farmers. C there will be a shortage of apples. Market for wheat price dollars tools pspf price.