Price Floor Generate

Which of these is the most likely to create a surplus of an item.
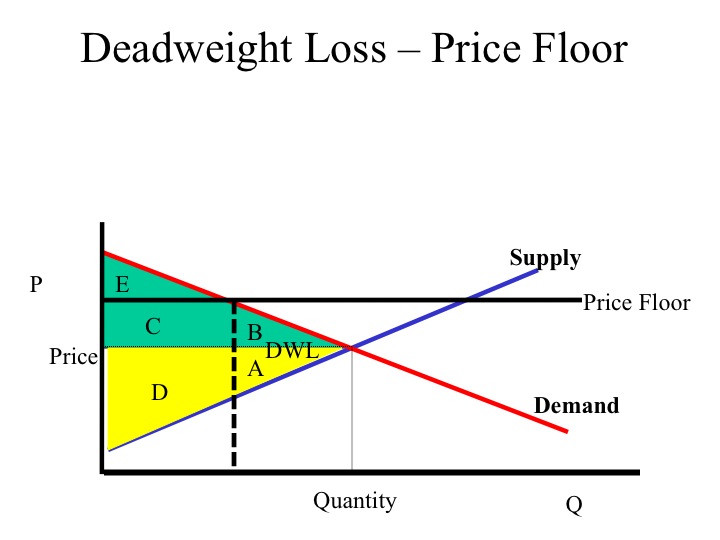
Price floor generate. This graph shows a price floor at 3 00. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. Price floors can also be set below equilibrium as a preventative measure in case prices are expected to decrease dramatically. Price supports sets a minimum price just like as before but here the government buys up any excess supply.
By observation it has been found that lower price floors are ineffective. A price floor or a minimum price is a regulatory tool used by the government. The government sets a limit on how high a price can be charged for a good or service. It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. When a price floor is put in place the price of a good will likely be set above equilibrium. A few crazy things start to happen when a price floor is set.
This is even more inefficient and costly for the government and society as a whole than the government directly subsidizing the affected firms. Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour wage market. T f a target price is the goal of a price floor or a price ceiling. But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
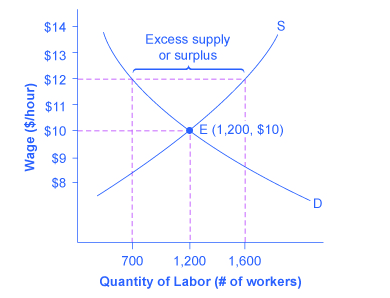
An example of a price floor would be minimum wage. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. Which of these describes the effects of price floors on the u. More specifically it is defined as an intervention to raise market prices if the government feels the price is too low.
First of all the price floor has raised the. A numerical limit on the quantity of a good that can be imported is a. Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply. Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
They can set a simple price floor use a price support or set production quotas. Drawing a price floor is simple. For markets to generate the greatest benefit and function in the most efficient manner they must. This set is often in folders with.
The graph below illustrates how price floors work. You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example. In such situations the quantity supplied of a good will exceed the. An example of a price ceiling would be rent control setting a maximum amount of money that a landlord can.













:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhyYouCantInfluenceGasPrices3-257334e47bc54cd7a449da9df90814af.png)