Price Floor Economics Example

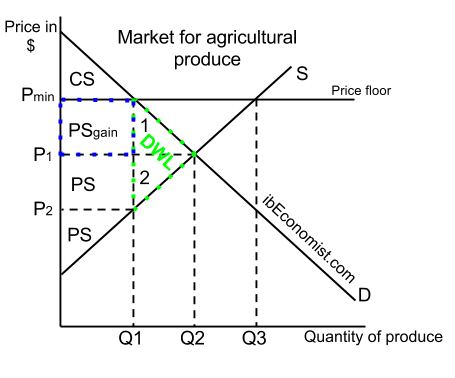
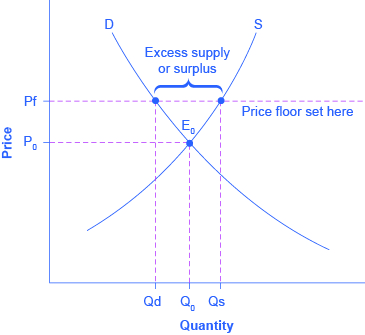
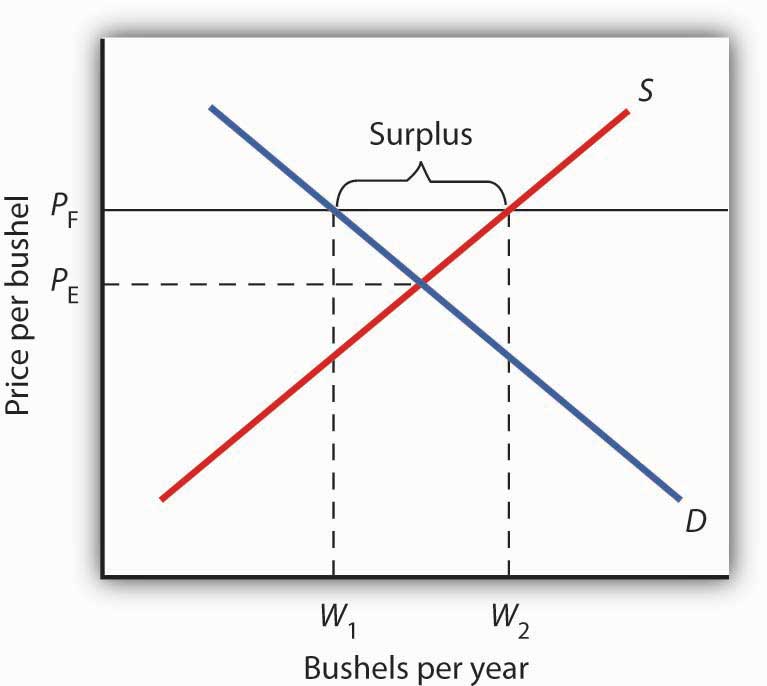
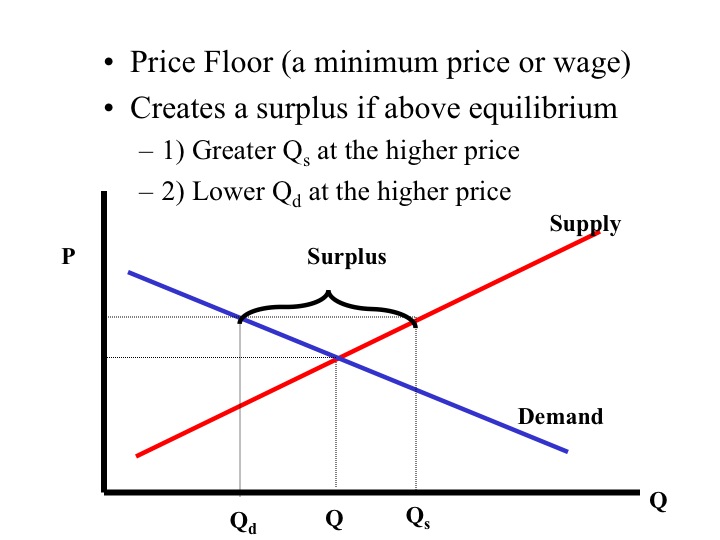
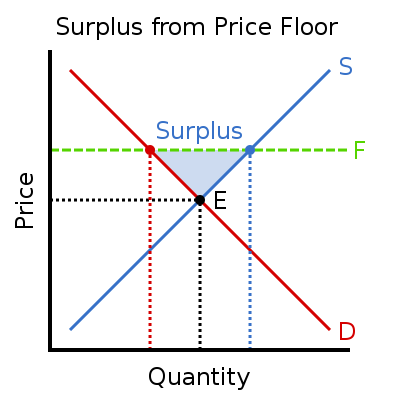
You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example.
Price floor economics example. A price floor in economics is a minimum price imposed by a government or agency for a particular product or service. Small farmers are very sensitive to changes in the price of farm products due to thin margins profit margin in accounting and finance profit margin is a measure of a. For example the uk government set the price floor in the labor market for workers above the age of 25 at 7. A good example of this is the farming industry.
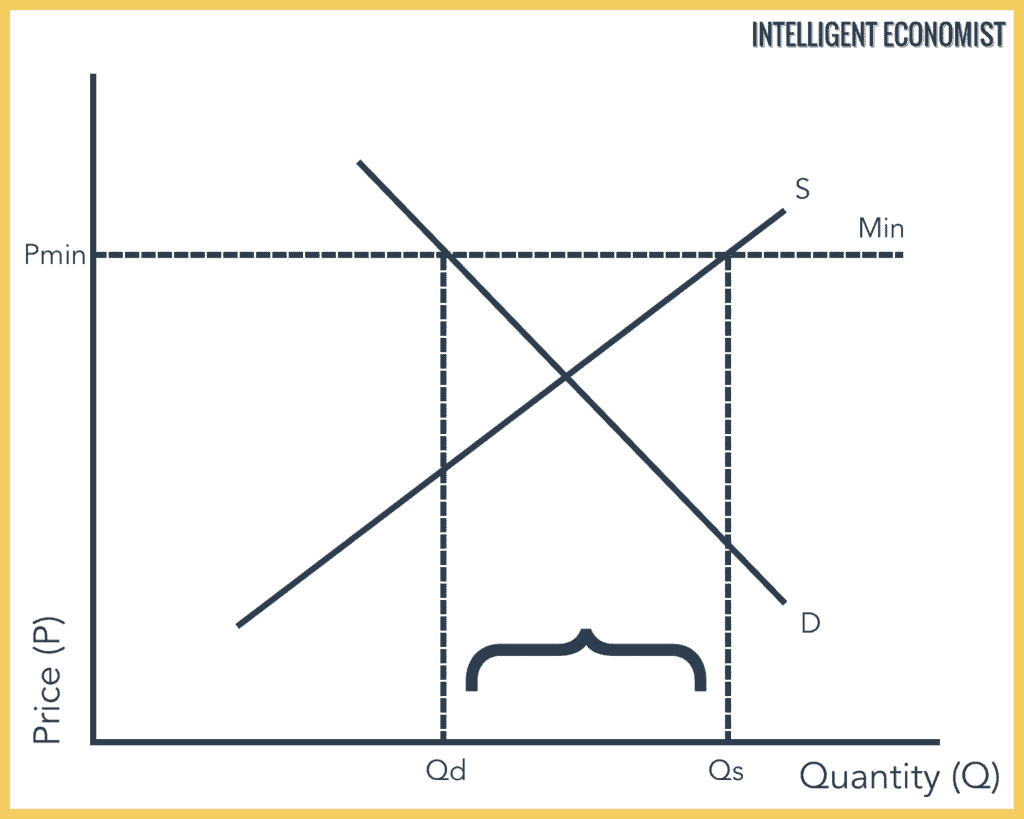
Drawing a price floor is simple. Price floors impose a minimum price on certain goods and services. In this case the supply for employment is greater than the demand of jobs due to the price control that creates a surplus. Price floors are effective when set above the equilibrium price.
Similarly a typical supply curve is. They are usually put in place to protect vulnerable suppliers. Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the view that someone working full time should be able to afford a basic standard of living. A price floor is the lowest price that one can legally charge for some good or service.
A price floor means that the price of a good or service cannot go lower than the regulated floor. A minimum wage law is the most common and easily recognizable example of a price floor. Demand curve is generally downward sloping which means that the quantity demanded increase when the price decreases and vice versa. A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group.
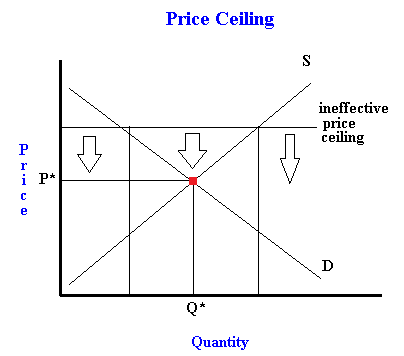
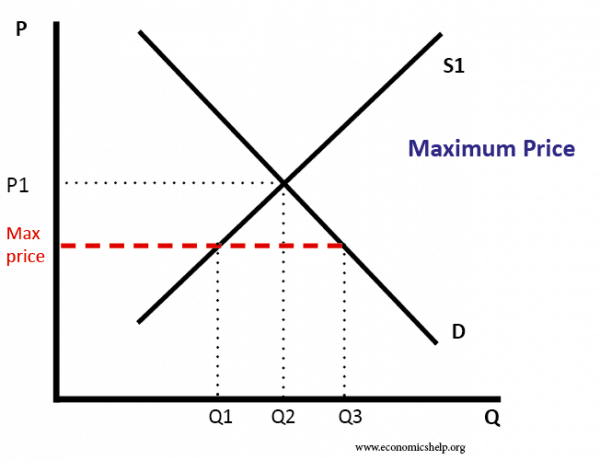
A price floor is the other common government policy to manipulate supply and demand opposite from a price ceiling. A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market. A price floor is the lowest possible price for something typically set by legal jurisdiction or regulation in order to change the equilibrium price. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
A price floor helps to buffer some of the human cost and serves the public good which a truly free market structure may inadvertently harm. Common examples of price floors are the minimum wage. Demand for the commodity equals the producers supply law of supply the law of supply is a basic principle in economics that asserts. A few crazy things start to happen when a price floor is set.