Price Floor Definition Microeconomics

Price floors are common government tools used in regulating.
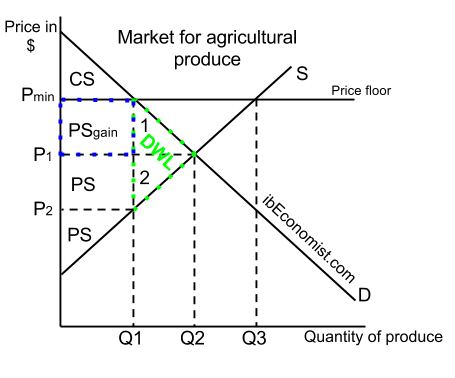
Price floor definition microeconomics. Small farmers are very sensitive to changes in the price of farm products due to thin margins profit margin in accounting and finance profit margin is a measure of a. Price floor in economics. Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. They are usually put in place to protect vulnerable suppliers.
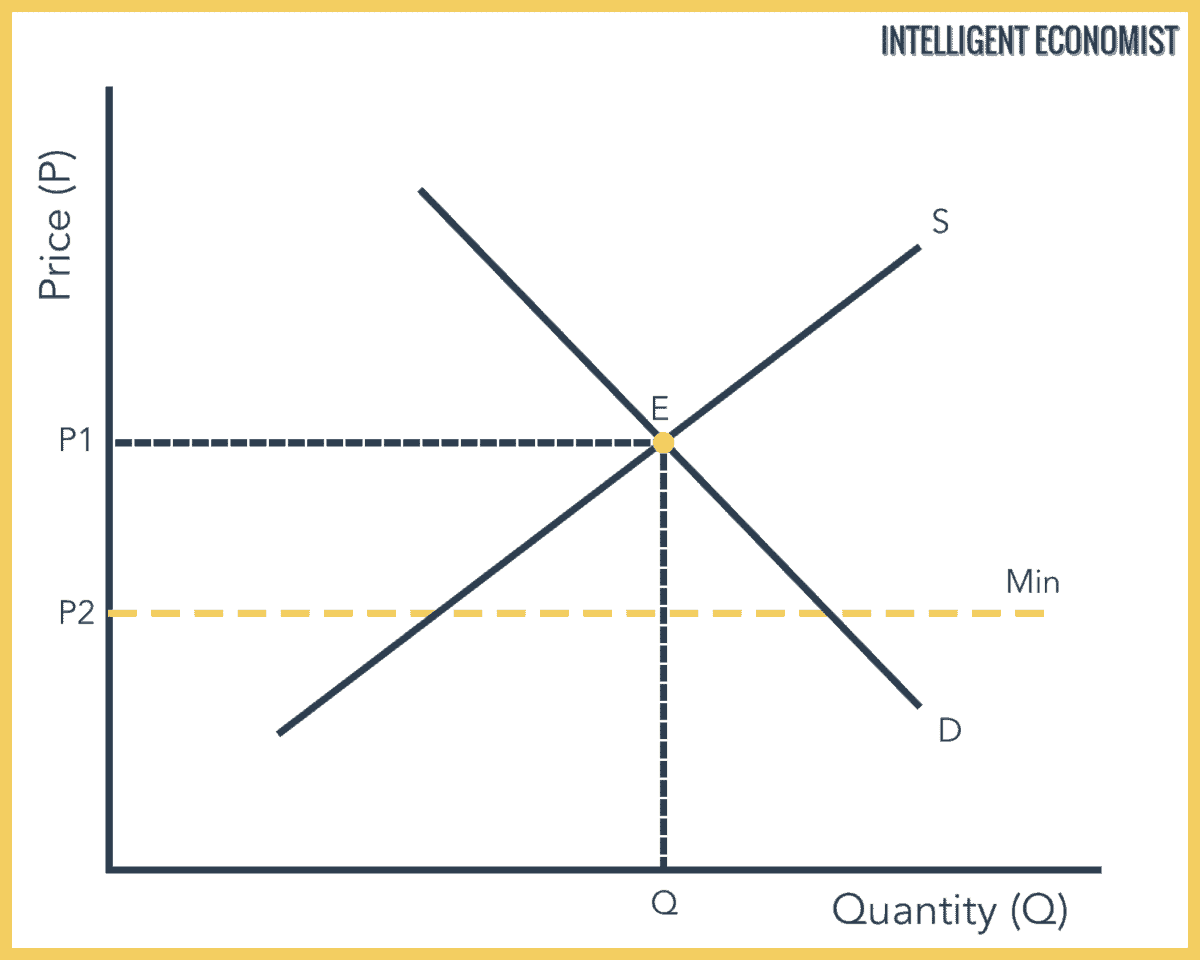
Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the normative view that someone working full time ought to be able to afford a basic standard of living. While it has good intentions the actual outcome could potentially differ severely. When the price floor in this case the minimum wage is set the demand falls substantially even as the supply in the market is still rather high. Economics microeconomics.
Minimum wage and price floors. A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at. A price floor is the lowest legal price that can be paid in markets for goods and services labor or financial capital. Price ceilings and price floors.
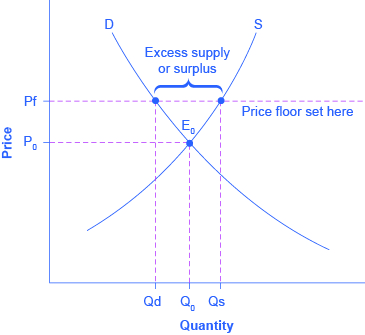
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor. How price controls reallocate surplus. We looked at the role of price floors and ceilings on market equilibrium. The pitfalls of the minimum wage is clearly indicated through graph 1 1.
A price floor is the lowest price that one can legally pay for some good or service. Price floors impose a minimum price on certain goods and services. A price floor is the other common government policy to manipulate supply and demand opposite from a price ceiling a price floor means that the price of a good or service cannot go lower than the regulated floor. Price and quantity controls.
Taxation and dead weight loss. This is the currently selected item. A price floor is the lowest price that one can legally charge for some good or service. We saw how price ceilings act to limit prices but often cause a.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers. The effect of government interventions on surplus. Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour wage market. Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the view that someone working full time should be able to afford a basic standard of living.
By observation it has been found that lower price floors are ineffective. A good example of this is the farming industry.