Price Floor Below The Equilibrium
Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price.
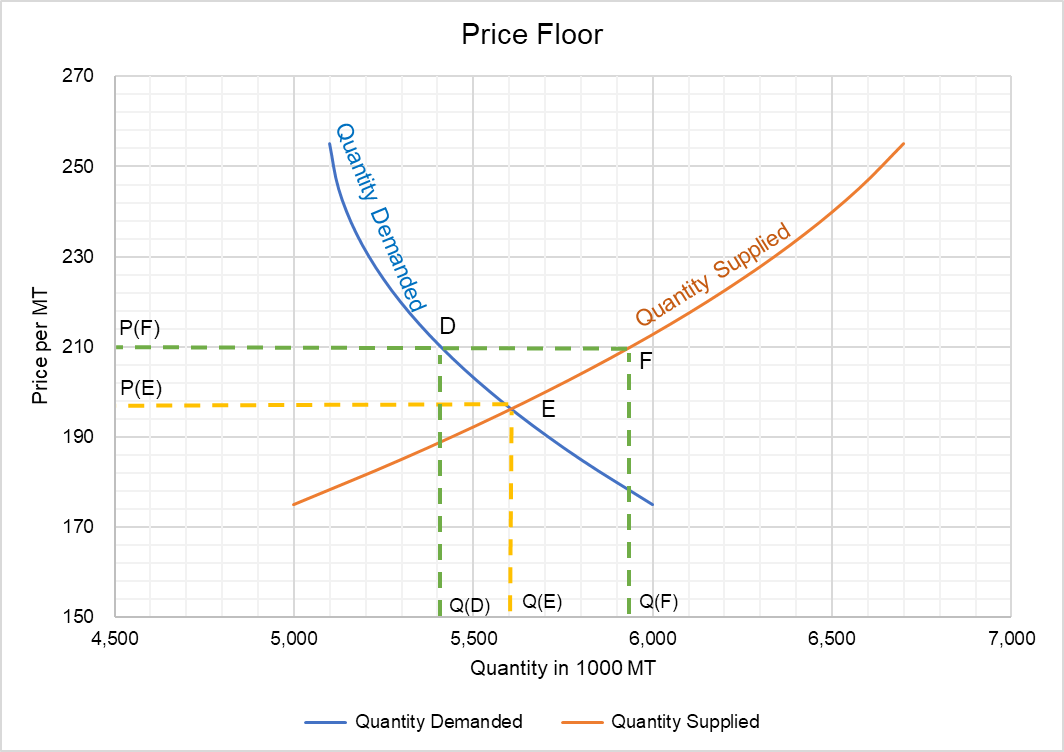
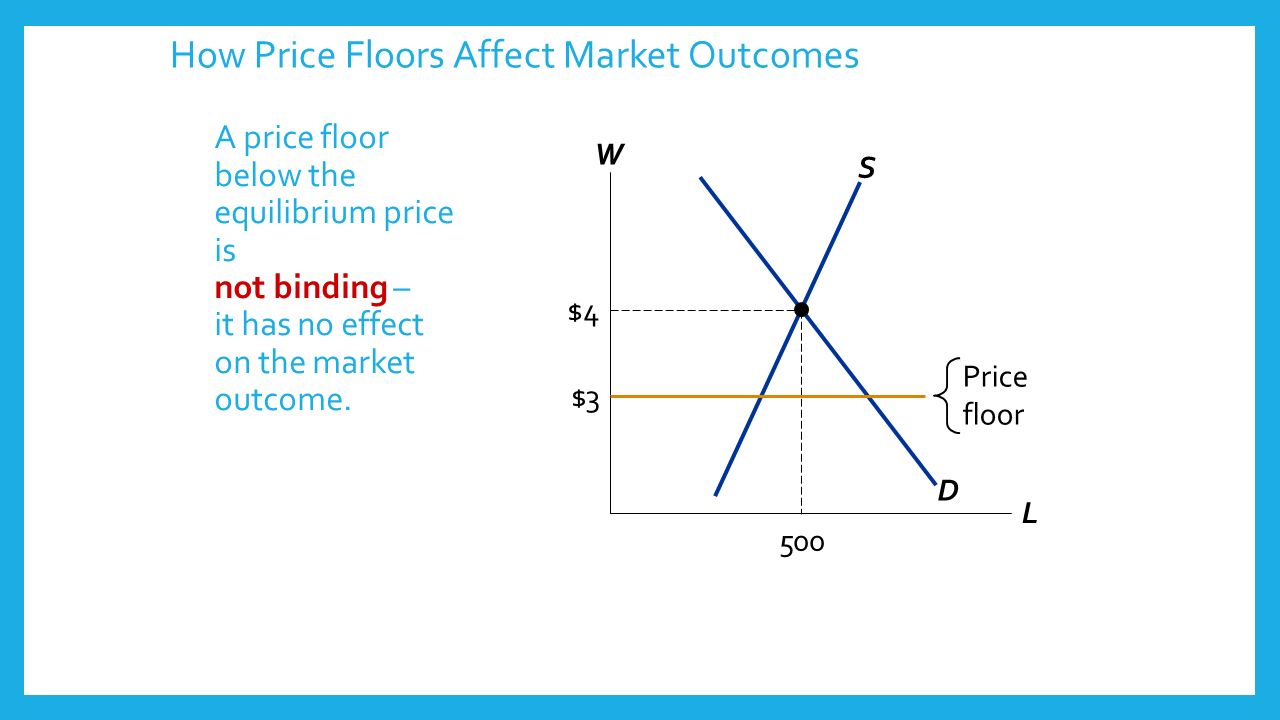
Price floor below the equilibrium. Price floors can also be set below equilibrium as a preventative measure in case prices are expected to decrease dramatically. In this case the floor has no practical effect. For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price. Drawing a price floor is simple.
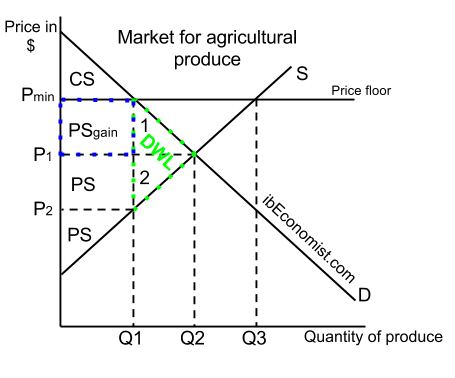
Around the world many countries have passed laws to create agricultural price supports. For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price. Price floors are sometimes called price supports because they support a price by preventing it from falling below a certain level. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
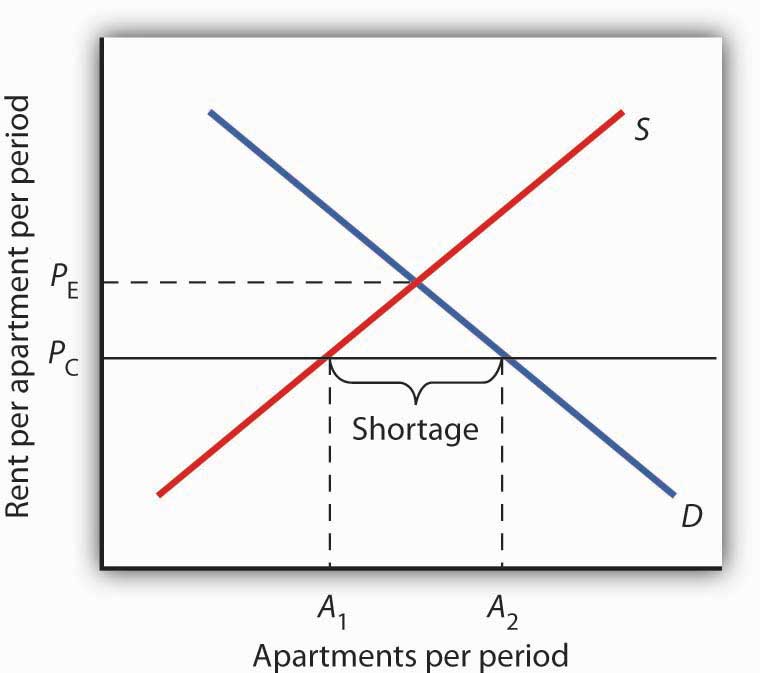
A price ceiling creates a shortage when the legal price is below the market equilibrium price but has no effect on the quantity supplied if the legal price is above the market price a price ceiling below the market price creates a shortage causing consumers to compete vigorously for the limited supply limited because the quantity supplied declines with price. If a price floor is set below equilibrium. In the first graph at right the dashed green line represents a price floor set below the free market price. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result.
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold is called a price a. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. In such situations the quantity supplied of a good will exceed the quantity demanded resulting in a surplus. If the minimum wage is a binding price floor then.
Price ceilings and price floors can cause a different choice of. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. A price floor could be set below the free market equilibrium price. A it will have no effect on the market.
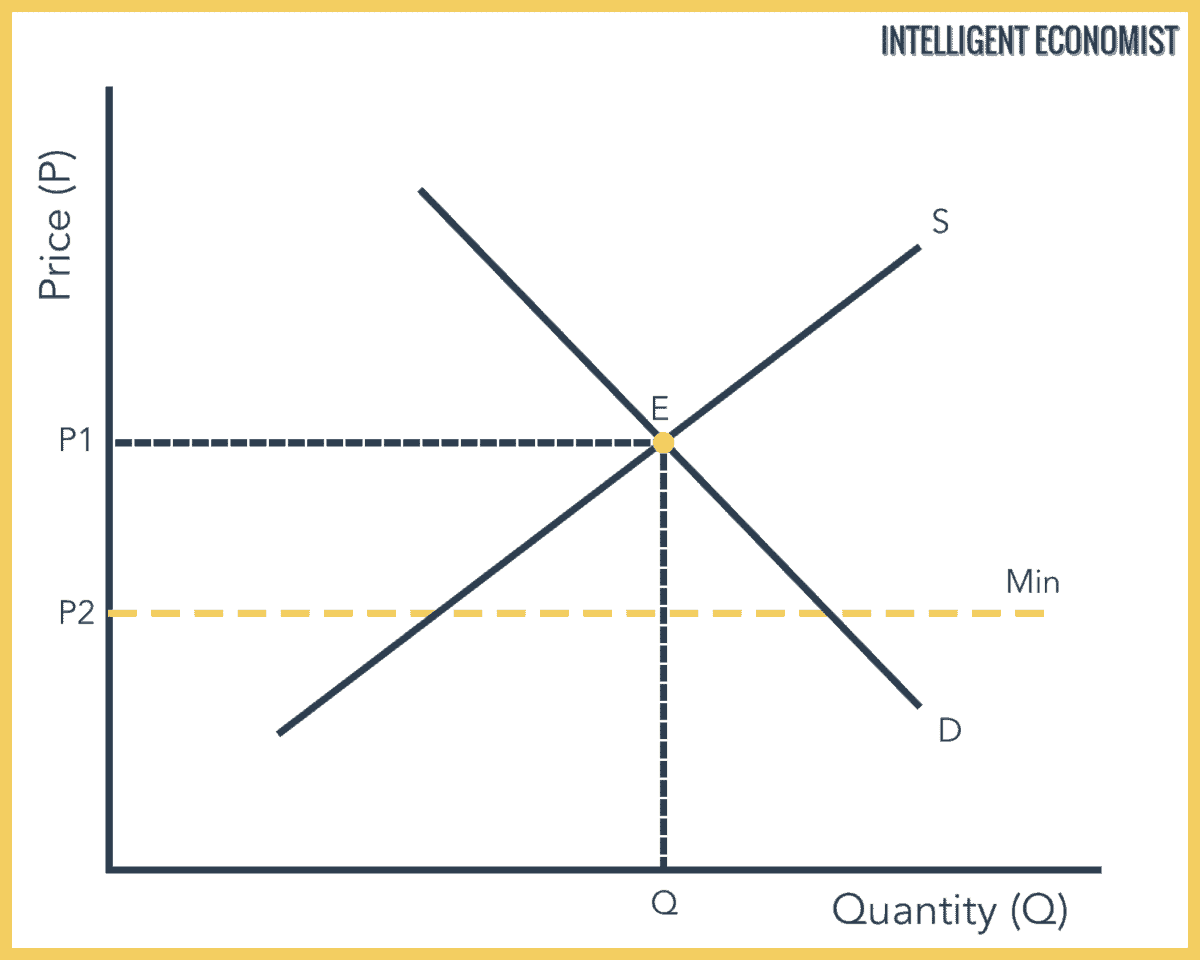
In the diagram above the minimum price p2 is below the equilibrium price at p1. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. The equilibrium price is above the price floor. Producers won t produce as much at the lower price while consumers will demand more because the goods are cheaper.
More than one of the above is correct. C a surplus will result. When a price floor is put in place the price of a good will likely be set above equilibrium. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
D the floor will be binding. The government has mandated a minimum price but the market already bears and is using a higher price. It has no legal enforcement mechanism. In other words they do not change the equilibrium.
A there will be a job for everyone who wants to work. The equilibrium price is below the price floor.