Price Floor Below Market Equilibrium
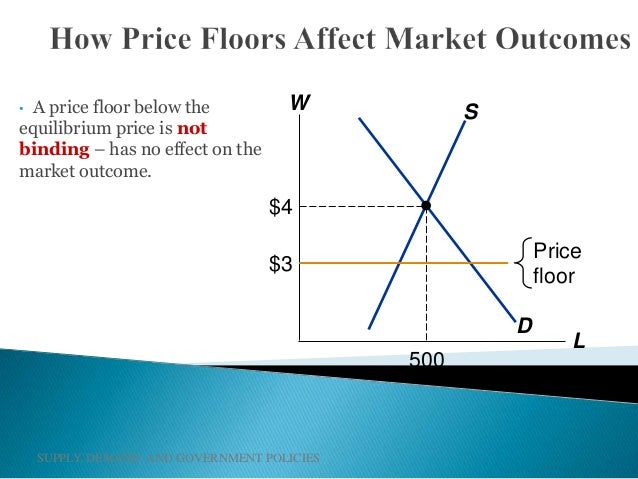
In this case the floor has no practical effect.
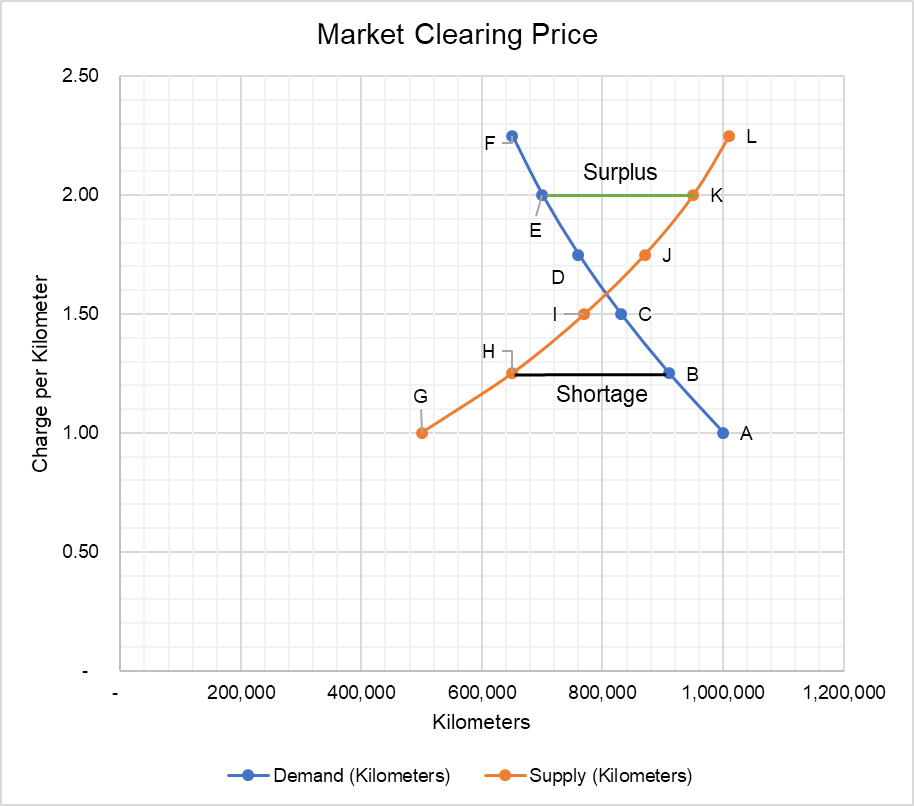
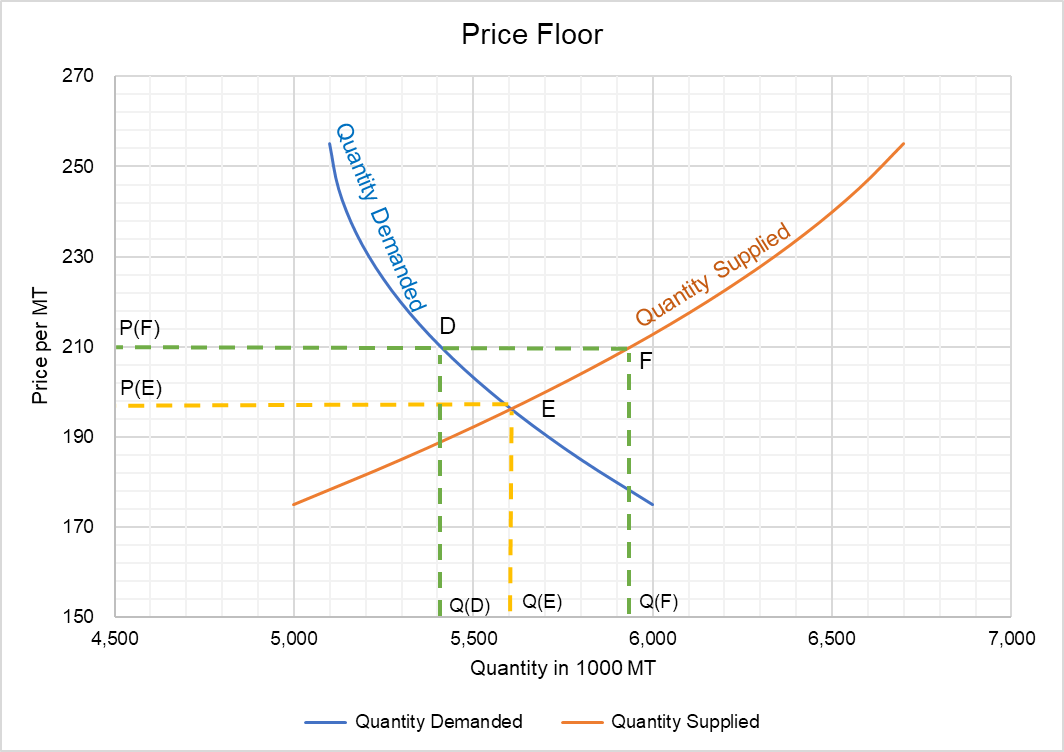
Price floor below market equilibrium. Therefore surplus drives price down. The government has mandated a minimum price but the market already bears and is using a higher price. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level. For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
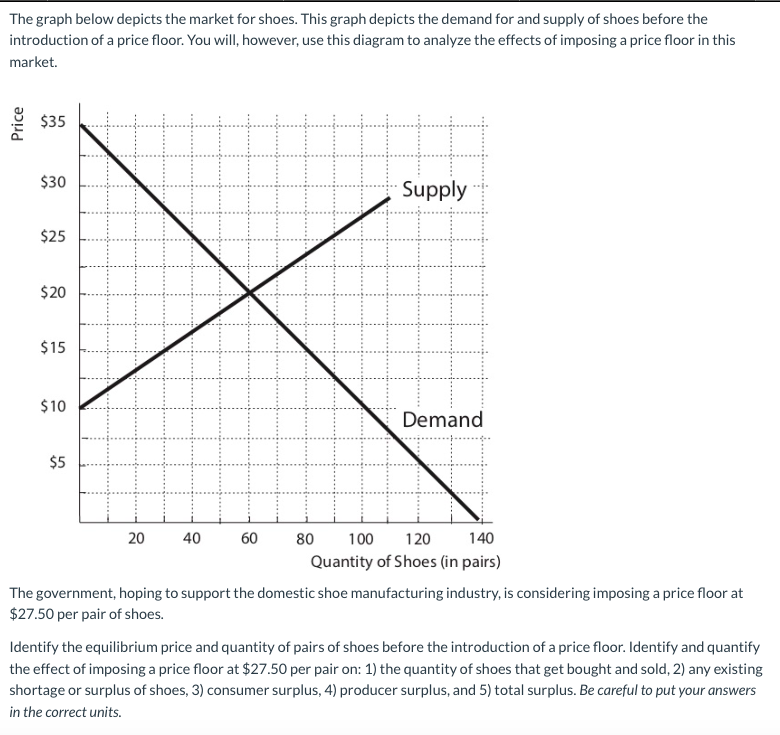
Producers won t produce as much at the lower price while consumers will demand more because the goods are cheaper. But if price floor is set above market equilibrium price immediate supply surplus can be observed. An increase in the supply of grain c. In a market economy which of the following would most likely cause a prolonged grain surplus.
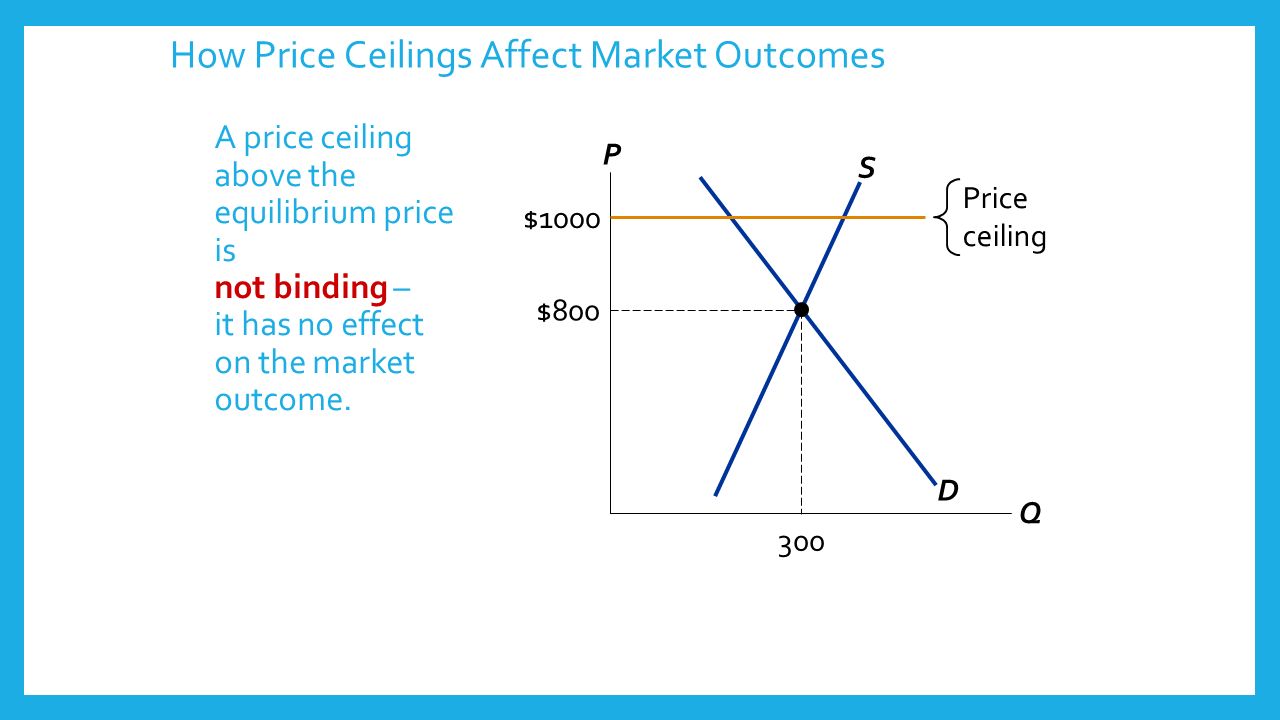
A decrease in the demand for grain b. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant. A price floor could be set below the free market equilibrium price. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
A non binding price floor is one that is lower than the equilibrium market price. The market is not clear. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant. Imposition of a price floor above the equilibrium price of grain d.
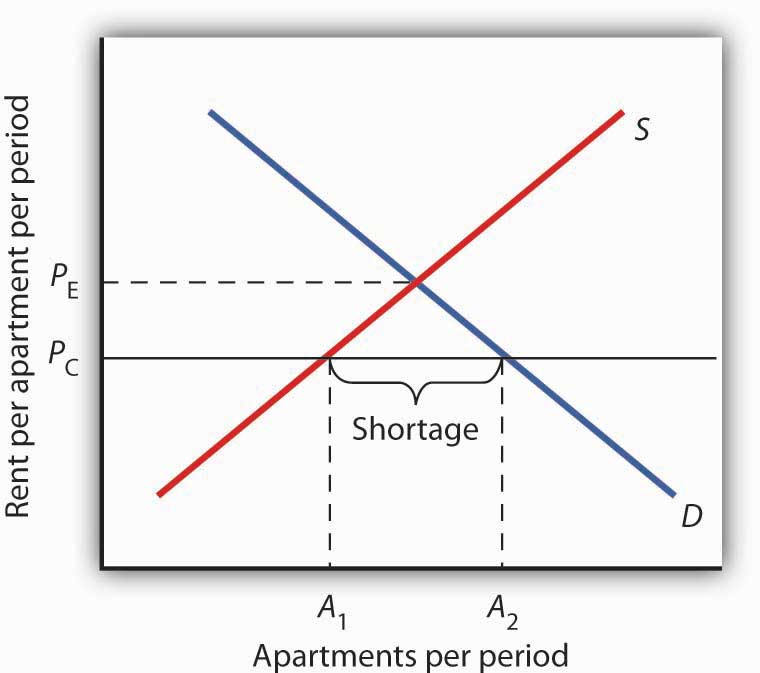
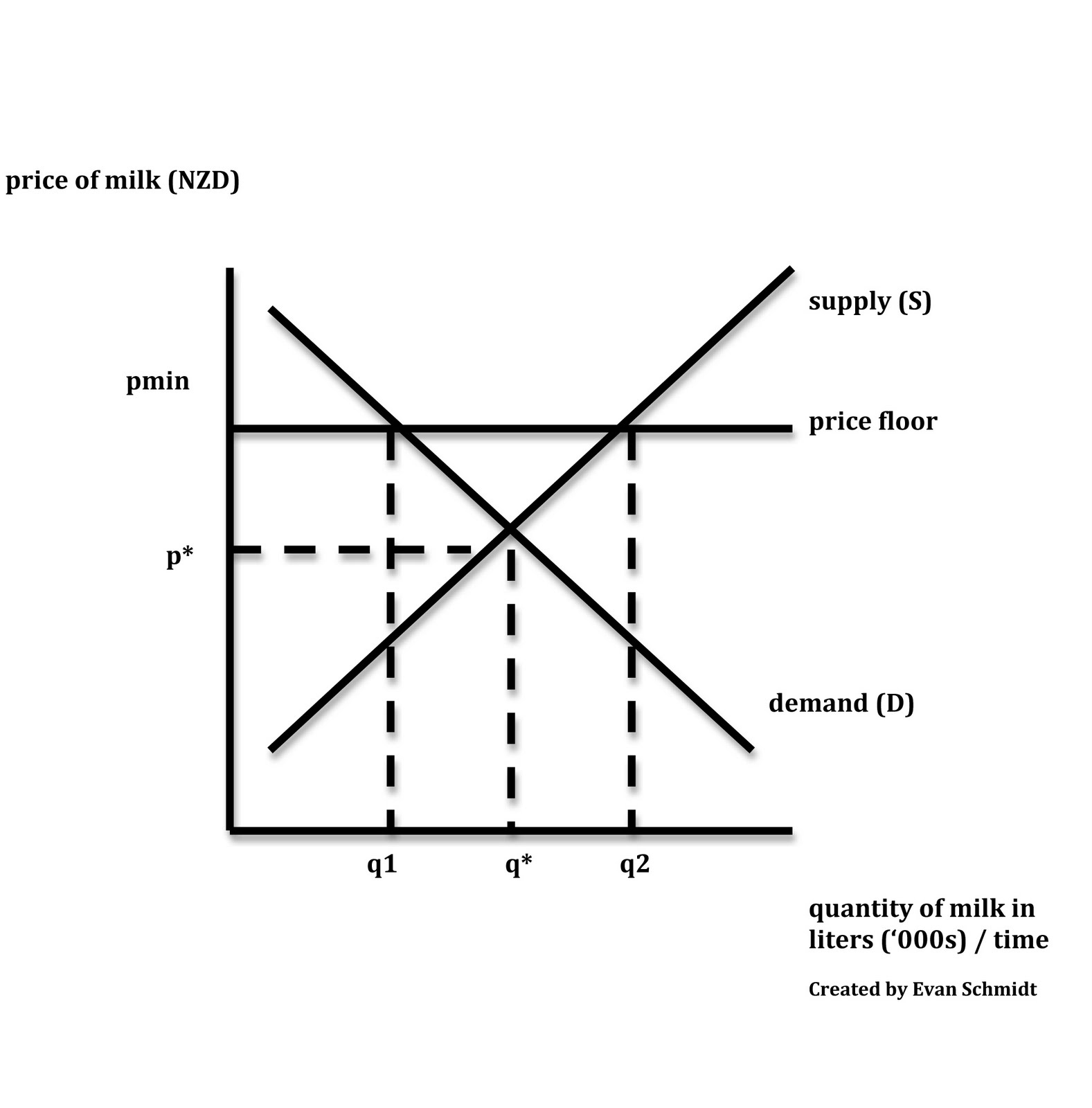
Imposition of a price ceiling below the equilibrium price of grain. The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result. Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price.
Drawing a price floor is simple. At higher market price producers increase their supply. In the first graph at right the dashed green line represents a price floor set below the free market price. Once you lower the price of your product your product s quantity demanded will rise until equilibrium is reached.
When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result. In the diagram above the minimum price p2 is below the equilibrium price at p1. Consider the figure below. If the market price is below the equilibrium price quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded creating a shortage.
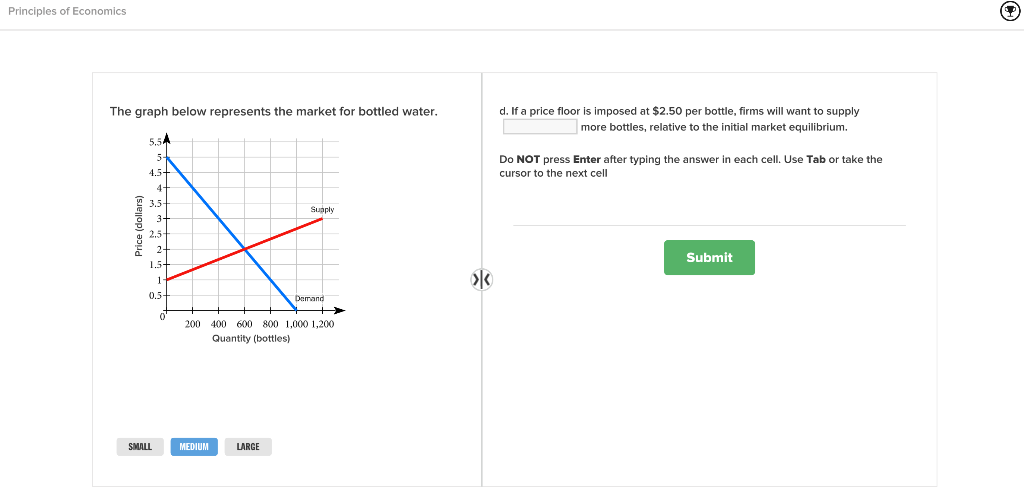
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price. In contrast consumers demand for the commodity will decrease and supply surplus is generated. If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.