Phase Transition Ceramic

Phase transition or phase change is the transition between solid liquid and gaseous states of matter as well as plasma in rare cases.
Phase transition ceramic. Study of the pzt ceramic gives a dielectric constant ε. R 515 492 and a loss tangent tanδ 0 005. The enhancement in the electric field induced strain is attributed to the rhombohedral to pseudocubic phase. Zirconium dioxide is one of the most studied ceramic materials.
Phase transition and piezoelectricity of bazro 3 modified k na nbo 3 lead free piezoelectric thin films jin luo state key laboratory of new ceramics fine processing school of materials science and engineering tsinghua university beijing china. Knl 0 03 n bnz ceramic has a lower t o t and a higher coexistence proportion of o t phase. Knl 0 03 n bnz ceramic has a high t c while achieving high piezoelectric. Zro 2 adopts a monoclinic crystal structure at room temperature and transitions to tetragonal and cubic at higher temperatures.
R t the curie temperature t. Vanadium dioxide vo 2 is a well studied mott insulator because of the very abrupt physical property switching during its semiconductor to metal transition smt around 341 k 68 c in this work through novel oxide metal nanocomposite designs i e au vo 2 and pt vo 2 a very broad range of smt temperature tuning from 323 5 to 366 7 k has been achieved by varying the. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties during a phase transition of a given medium certain properties of the medium change often discontinuously as a result of the change of external conditions such. Measurement at high temperatures permit to determine from the maximum of ε.
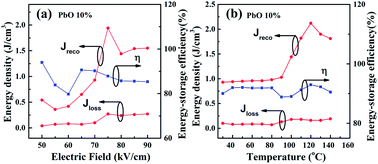
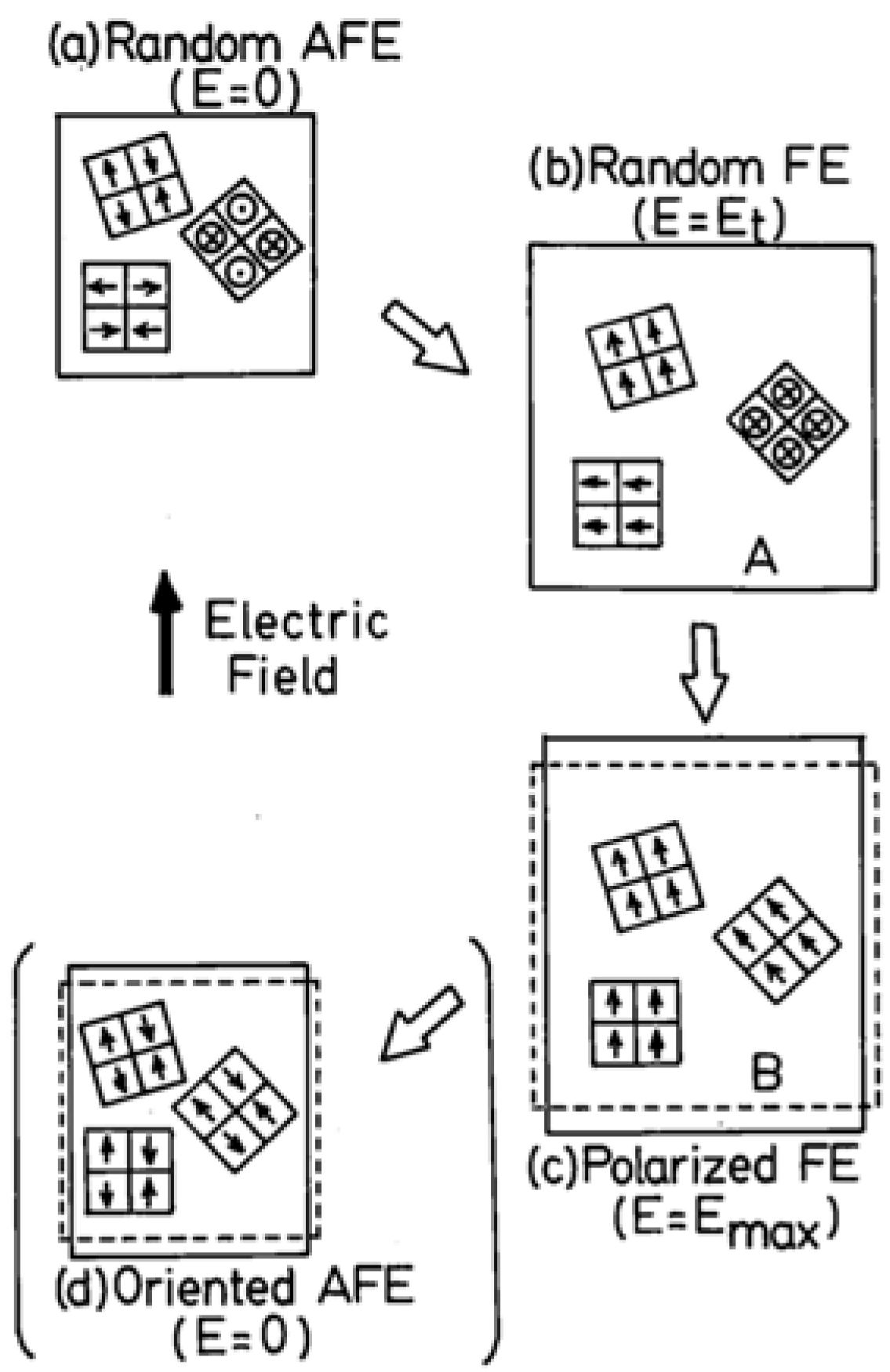
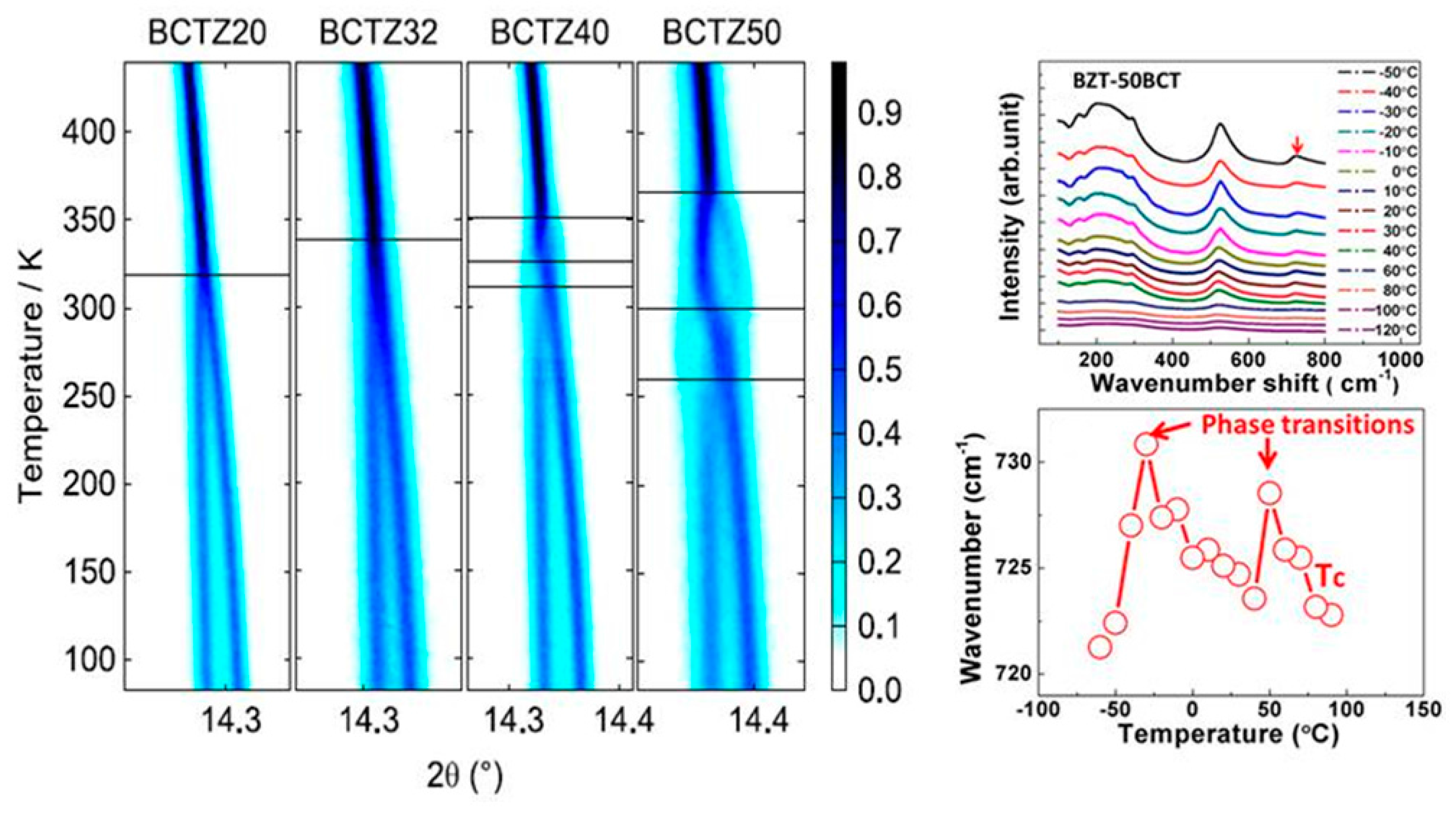
C 380ºc of the ferroelectric paraelectric phase transition of pzt ceramic. Knowledge of such properties as the thermal length change for the sintering of technical ceramics phase transitions and the specific heat capacity for modified glass and the precise thermal conductivity values for inorganic building materials is of high practical importance in this field. Another important aspect is the reversibility of the e field induced phase transition in several afe compositions the induced fe phase remains stable even after the e field is removed irreversible transition resulting in the absence of a double polarization hysteresis loop a typical example is the plzst system where the reversibility of the afe fe phase transition is tailored by changing. The phase transition temperature t o t and t c of the ceramics were shifted by li doped.
The change of volume caused by the structure transitions from tetragonal to monoclinic to cubic induces large stresses causing it to crack upon cooling from high temperatures. The highest proportion of two phases coexistence is the most efficient.

.jpg)