Paediatric Orbital Floor Fractures

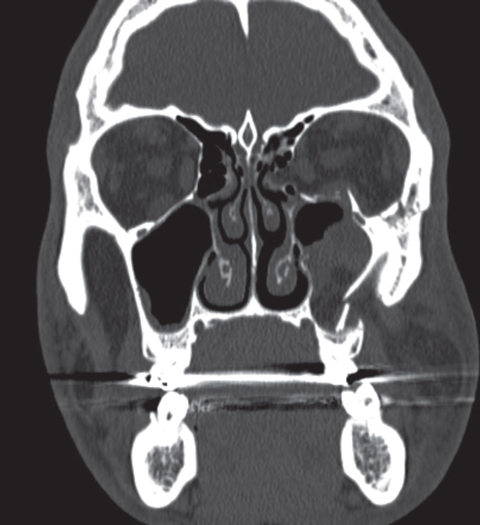
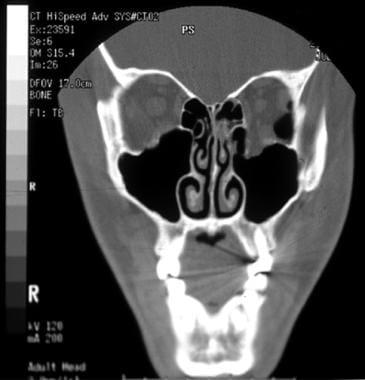
The most characteristic orbital blowout fracture in children although it is relatively uncommon among pediatric facial fractures is the so called trapdoor fracture 16 17.
Paediatric orbital floor fractures. 8 they are often related to sports. A lack of external signs such as oedema or ecchymosis often misleads physicians into underestimating the. Wei la 1 durairaj vd. Pediatric orbital floor fractures can present differently than adult orbital floor fractures and can have adverse long term consequences if not recognized and dealt with appropriately.
In summary pediatric orbital floor fractures are rare in very young children becoming more frequent after the age of 7 years. Because the presentation of the injury is usually more subtle in children a high index of suspicion is needed to make the diagnosis particularly when diplopia accompanies a suggestive history of mechanism. To summarize the unique aspects of orbital floor fractures in children with regard to clinical presentation management and outcomes. Patients commonly present with acute fractures to the emergency department and delayed diagnosis can result in significant morbidity.
Pediatric orbital floor fractures. Orbital injuries warranting surgical intervention are infrequent in the paediatric population but blowout trap door fractures are unique in children and may constitute a relative surgical emergency. This is a green stick fracture in which a bone fragment protrudes into the sinus while remaining stably attached by a hinge of mucoperiosteum to the intact part. Harris gj garcia gh logani sc murphy ml.
Pediatric orbit fracture patterns are dictated by the age of the patient with respect to their craniofacial morphology and mechanism of injury. Trapdoor fractures otherwise known as white eyed blowout fractures occur predominantly in the paediatric cohort and have a male predilection. Clinically low velocity but high force crush injuries are the most common cause of orbital floor fractures in children. 1 department of ophthalmology university of colorado school of medicine denver colorado usa.
Children presenting with floor or medial wall fractures are at high risk of entrapment as paediatric bones are more prone to greenstick fracture which then creates a trapdoor effect ensnaring the inferior oblique and inferior rectus muscles or other orbital contents. Recent findings the most common problem among patients requiring surgical revision of a previously repaired orbital floor fracture is an improperly placed orbital floor implant usually erroneously placed under the posterior bony ledge. A retrospective review of isolated orbital floor fractures at the royal children s hospital of melbourne over a 10 year period was undertaken to evaluate the outcome of those patients who. Pediatric orbital floor fracture.
Purpose of review the current study reviews the recent literature on pediatric orbital blowout fractures and provides guidelines on their management. Correlation of preoperative computed tomography and postoperative ocular motility in orbital blowout fractures.